How to Calculate Customer Acquisition Cost & How to Reduce it?
- April 20, 2022
- 10 mins read
- Listen

Table of Content
Did you know that it costs five times as much to attract a new customer, than to keep an existing one?
The first rule of any business is to retain customers and build a loyal relationship with them, and thereby avoid customer acquisition costs.
Customer acquisition cost (CAC) has become a crucial business metric as it helps businesses determine the resources they will need to attract new customers and continue their growth.
Acquiring your first customer is a great milestone for every business. While it’s no secret that getting people to buy from you is critical, you also need to focus on long-term growth tactics if you want to maintain growth.
For any company, thinking about your customer acquisition cost (CAC) can be confusing, frustrating, and perhaps a bit scary.
But it really doesn’t have to be.
Customer acquisition cost is hence the amount of money your company spends to acquire customers. It also helps in measuring the return on investments on the efforts it took to grow your business’s clientele.

If you want your business’s customer base to expand and still make net profits, it is essential for you to understand all that there is to know about customer acquisition costs in marketing.
The following article will be covering the following topics for the same reason:
– Definition of Customer Acquisition Cost
– Formula of Customer Acquisition Cost
– How to Calculate Customer Acquisition Cost?
– Customer Acquisition Cost vs Lifetime Value (CLTV)
– Customer Retention vs Acquisition Cost
– Customer Acquisition Cost by Industry
Definition of Customer Acquisition Cost
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) refers to the total resources and costs incurred for acquiring a new customer.
It encompasses the cost of acquiring business across all your marketing efforts—online and offline, billboards and media placements, Google Ads and Facebook ads, even the cost of a store-front sign over a specific period of time to acquire new customers.
Customer acquisition professionals use specific strategies & techniques to get potential customers to take action. The main goal is to create a systematic, sustainable customer acquisition framework to acquire new customers and grow revenue for the business.
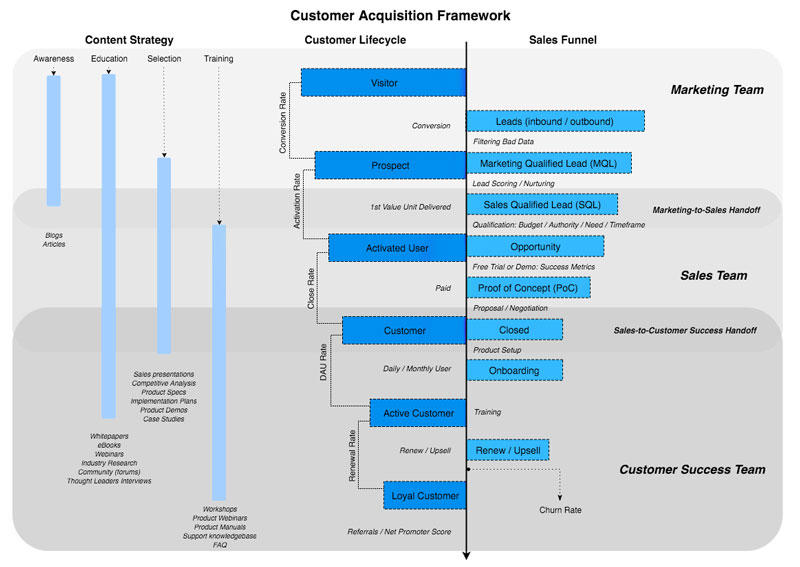
Ideally, the customer acquisition cost should be as low as possible; however, there are a number of factors that affect CAC like brand awareness and your existing ways of marketing.
Formula of Customer Acquisition Cost
Customer acquisition cost (CAC) shows the exact cost to acquire new customers and how much value they bring to your business. When combined with customer lifetime value (CLV), the metrics helps companies determine how viable their business model is.
For calculating customer acquisition cost, you need to know the following.
- Total amount spent on acquiring new customers (TS): It can include spending on sales, marketing, and revenue operations in a given time period
- Total number of new customers acquired (TNC)
The sum of these costs is then divided by the number of customers you acquired.
Hence, the formula for calculating CAC is really quite simple:

How to Calculate Customer Acquisition Cost?
Calculating customer acquisition involves keen observation of costs involved in the sales and marketing efforts made by the business.
Let’s explain the calculation process with examples for better understanding.
Example 1:
Take a 30-day snapshot of your business and add up all of the costs that were associated with sales and marketing efforts:
- Sales/marketing salaries
- Amount spend in advertising
- Tools/technology (CRM, email software, etc)
- Additional costs or overhead associated
Once you add up all of these expenses. Suppose it totaled $15,000 over a 30-day period. After that, you have to divide the cost by the number of customers that you gained within that particular period.
Let’s say 150 customers over the last 30 days.
Hence CAC = $15,000 / 150
The CAC = $100
Example 2:
If you are spending $200,000 to acquire 200 customers, then results will be as follows:

The total cost of customer acquisition will be $1000.
It is probably obvious that the lower customer acquisition cost is generally better. But there is no one-size-fits-all amount that makes sense for every business.
Customer Acquisition Cost vs Lifetime Value (CLTV)
Both the metrics are vital and both tell how effectively your business is being run, where you are losing money, and where you can improve.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) is perhaps the more coveted metric because it helps you understand bottom line profit, but, as we discussed, you can’t know your CLV unless you know how much it costs to acquire a customer.
By using these metrics in tandem to generate a more holistic understanding of performance—and remember, don’t be afraid to break each out into more granular measurements of specific parts of your business.
The customer acquisition cost to customer lifetime value, CAC:CLTV ratio measures the relationship between the lifetime value of a customer, and the cost of acquiring that customer.
Customer lifetime value tells you the amount of money your customers are paying. It is an important metric because it helps in projecting your company’s worth to competitors and potential customers.
The metric is computed by dividing LTV by CAC. It is a signal of customer profitability, and of sales and marketing efficiency.

*ARPU refers to Average Revenue Per User
Here is an example for CAC vs CLTV.
Consider a SaaS company that had a gross margin of 75% and monthly customer churn of 2%, and each customer spent an average of $40 with you every month.
And the calculation would look like this:
75% X ( 1 / 2% ) X $40 = $1,500 CLTV
Note:
Measuring and optimizing the CAC metric can be challenging on a number of fronts, especially if you’re attempting to attribute acquisition costs to individual accounts or customer segments – how much of your monthly ad spend or sales budget should be attributed to a specific win?
Best practices:
- To reduce your CAC and optimize profit, companies need to optimize their funnel by quantifying each step of the process and understanding how many visits to leads, how many leads lead to opportunities, and how many opportunities lead to customers.
- It’s also important to optimize your pricing because a huge portion of CAC feeds into the recovery period, as well as CAC ratio.
Customer Retention vs Acquisition Cost
Many companies focus on the majority of their time and resources on acquisition. Efforts towards effective retention strategies are often neglected.
Though retention offers a much higher ROI on advertising spend for certain business models—and is often much more
cost-effective than its counterpart.
Should a business focus on acquisition or retention?
There is no cookie cutter answer to this question. Each company is different, and has unique needs, objectives, and circumstances.
Businesses that depend on large, one-time customer purchases more than repeat transactions may be better served by focusing on acquisition initiatives.
On the other hand, there are many situations in which retention should be the higher priority.
Customer retention cost (CRC) can be calculated by adding up all the costs required to retain customers over a given period and dividing by the number of customers retained during that period. These costs can be averaged over your entire customer base or calculated per customer.
The procedure for calculating CRC can be expressed through the formula:
CRC = Total costs for customer retention / Total number of customers retained
For example, if total customer retention costs for the year added up to $200,000 and you retained 5,000 customers, your average CRC for the year would be $40 per customer.
Customer Acquisition Cost by Industry
Your customer acquisition cost should lay at the center of your marketing strategy, and you should make decisions according to this metric. Customer acquisition costs vary across different industries because of various determining factors like:
- Length of the sales cycle
- Purchase value
- Purchase frequency
- Customer lifespan
- Company maturity
Without calculating the CAC, you won’t be able to make even the short-term plans for your product irrespective of any industry.
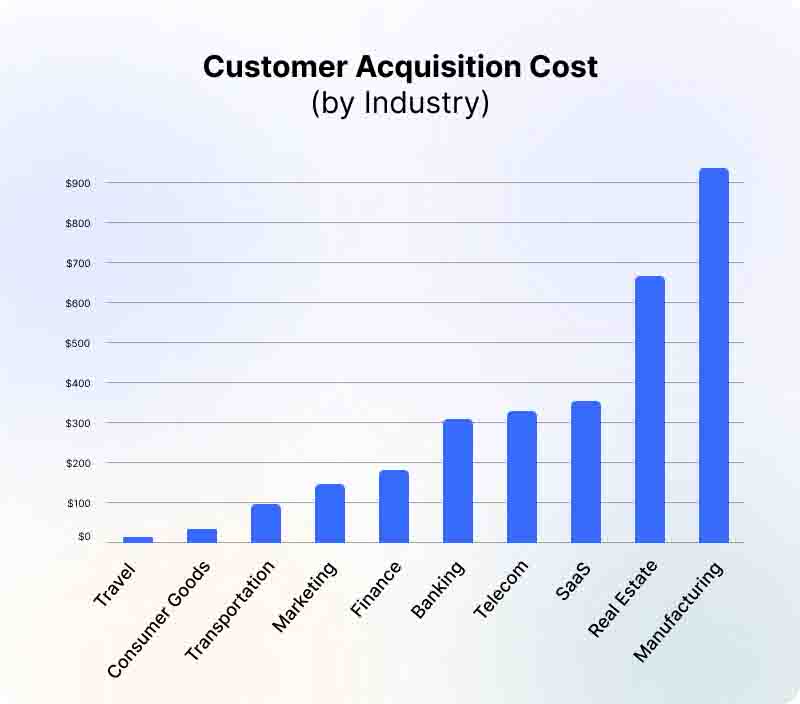
A good customer acquisition cost varies by the industry and tactics used. But a good way to benchmark your CAC is by comparing it to customer lifetime value. The customer acquisition cost based on different industries are as follows:
SaaS
The metric is very important in the SaaS industry as the entire business model revolves around the lifetime value of the customer. To acquire new customers, SaaS companies devote a substantial amount of time & money before they can see the complete return on their investment. The average organic CAC is $205 and inorganic CAC is $341.
Banking
Banks compete by bidding on display ad space in social networks, search engines, forums, FAQs and various affiliation websites. Most benchmarks say that the average customer acquisition cost (CAC) for the banking sector is above $300, a figure which has been rising due to the negative effects of Covid-19 and saturation of digital channels.
Real Estate
In the real estate industry where large real estate brands are unable to command a premium for their properties, customer acquisition cost metric serves as a true indicator of the brand’s value. A brand’s true worth could be better judged, in terms of its client acquisition cost. The average organic CAC is $660 and inorganic is $1,185. It’s easier to acquire and retain customers in this industry with a well-chosen real estate CRM, of which there are several tailored options. This can help drive down CAC substantially.
Travel
The average customer acquisition cost for the travel industry can be reduced by optimizing the landing page with a clear offer, highlighted CTA buttons, including genuine reviews. Also by using retargeting ads to connect with potential customers that have already engaged with you. However, the CAC for travel companies is $7.
Manufacturing
Knowing if you have a good customer acquisition cost for the manufacturing industry can be hard. Usually, the average inorganic CAC for manufacturing & distribution is $662 and the organic cost is $905.
Telecom
The CAC metric in the telecom industry gives insights into the total average cost of adding a new subscriber to your business list. The metric includes the expenses covering marketing and sales efforts, along with any additional spend on assets to acquire new subscribers. The CAC for the telecom industry is $315.
Consumer Goods
Suppose a consumer’s goods company spends $7,000 in sales and $3,000 in marketing to attract 1,000 new customers. Then it’s CAC= ($7,000 + $3,000) / (1,000) = $10. Thus, the consumer goods company spends $10 to acquire each new customer.
Transportation
For measuring the marketing effectiveness of the transport business, there are metrics to be used like leads, website traffic and conversions. The customer acquisition cost for transportation businesses is $98.
Finance
How much does it cost a financial institution to acquire a new customer? As per research, the average acquisition cost is $200. The customer acquisition strategies across the successful banks are the diversified and personalized methods of engagement across the entire customer journey. The cost of customer acquisition for the finance sector is $175.
Marketing
Improving marketing efficiency all comes down to identifying the most important moments to reach consumers and eliminating non-essential marketing spend. If you understand the online behavior of your target audience, and align with their way to purchase, you will certainly lower your acquisition costs. Usually, the CAC for marketing agencies is $141.
Summing Up
Customer acquisition cost is a very important business KPI. This metric is the lifeblood of any company, small or large. It helps us to know how much it costs your business to bring in new customers so that you would be able to make informed business decisions, as well as predict how profitable your company would be in the long run.
The companies succeed only when they put their customers in focus, for both acquisition and retention. Hence, defining a great acquisition strategy can help you not only to lower your customer acquisition cost but also increase your customer lifetime value.



